This article covers configuring the Wi-Fi Library Item in Kandji. For information about different network authentication types, please see our Network Authentication Overview article.
Add a Wi-Fi Library Item
To add this Library Item to your Kandji Library, follow the steps outlined in the Library Overview article.
Give the new Wi-Fi Library Item a Title. Use the title to differentiate this Library Item from other Wi-Fi Library Items. Use a name that identifies the item — for example, the title might include the SSID or the location where the Wi-Fi configuration is used.
Assign this Library Item to Blueprints containing devices you would like to deploy it to.
Configure General Settings
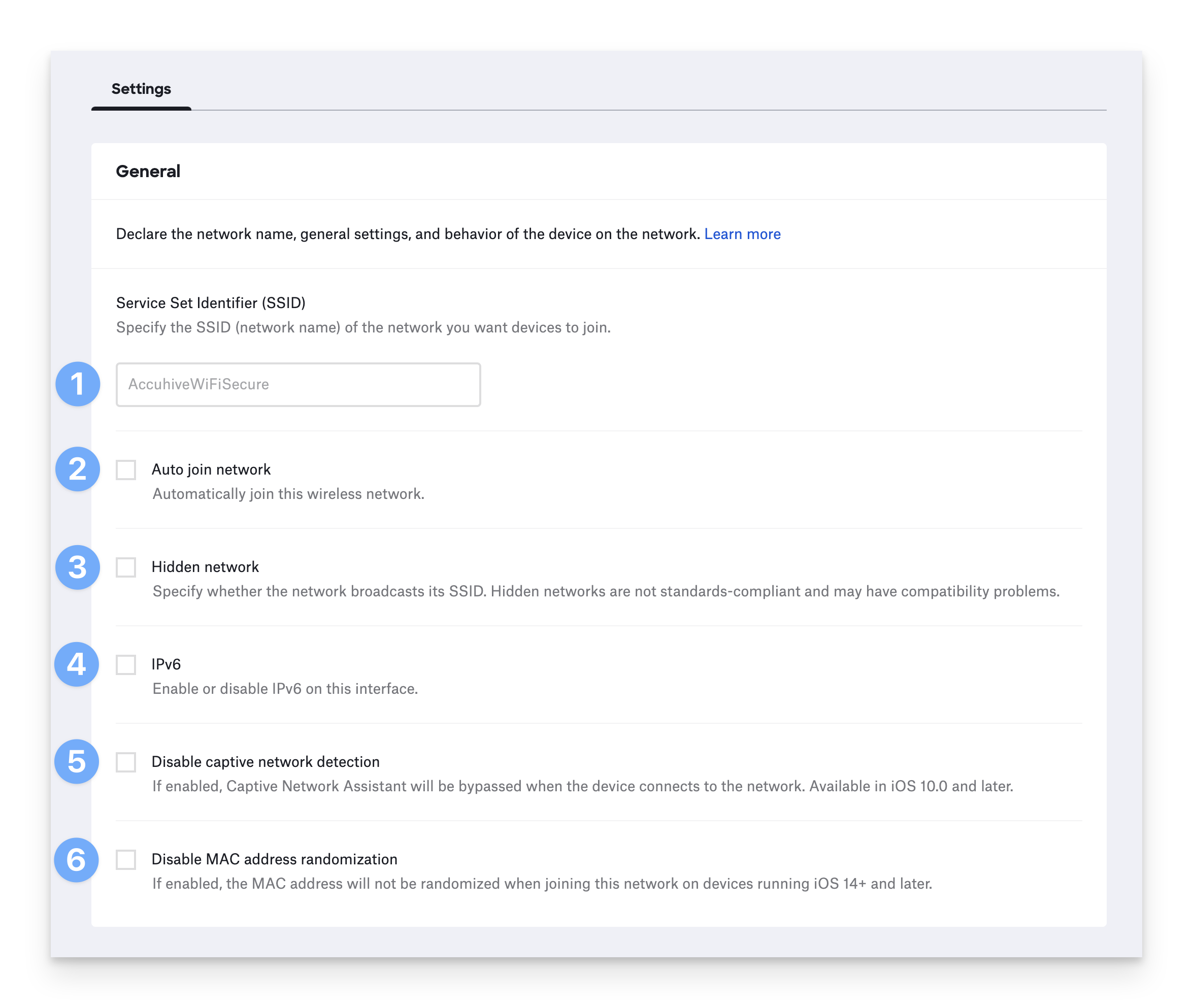
The General settings describe the network and device behavior unrelated to authentication.
Specify the Service Set Identifier (SSID), also known as the network’s name.
If you want devices to automatically join this network when it is available, select Auto join network. If you do not select Auto join network, devices will know how to connect to the network, but the user will have to choose to do so.
If the network is hidden—i.e., it does not broadcast its SSID—select Hidden network. Hidden networks are not standards-compliant and are not recommended.
To use IPv6 on this network, select IPv6.
If you do not want to use Apple’s Captive Network Assistant on this network, select Disable captive network detection.
If you wish to turn off MAC address randomization, select Disable MAC address randomization.
Configure Authentication Settings
The Wi-Fi Library Item supports pre-shared key (PSK, “personal”) authentication and 802.1X Extensible Authentication Protocol (EAP) authentication (often referred to as “enterprise Wi-Fi”). Most EAP types have additional settings that you need to configure. These settings become available when you select an EAP type. A network may support multiple authentication types, so you can choose more than one EAP type when configuring enterprise authentication.
Many older encryption protocols are no longer considered secure. Use the most up-to-date authentication and encryption supported by your network.
None
Use the None authentication type when no password is necessary to join the network. If a network with the specified SSID is available and does not require authentication, the device will attempt to join it.
Anyone can join a network with no password.
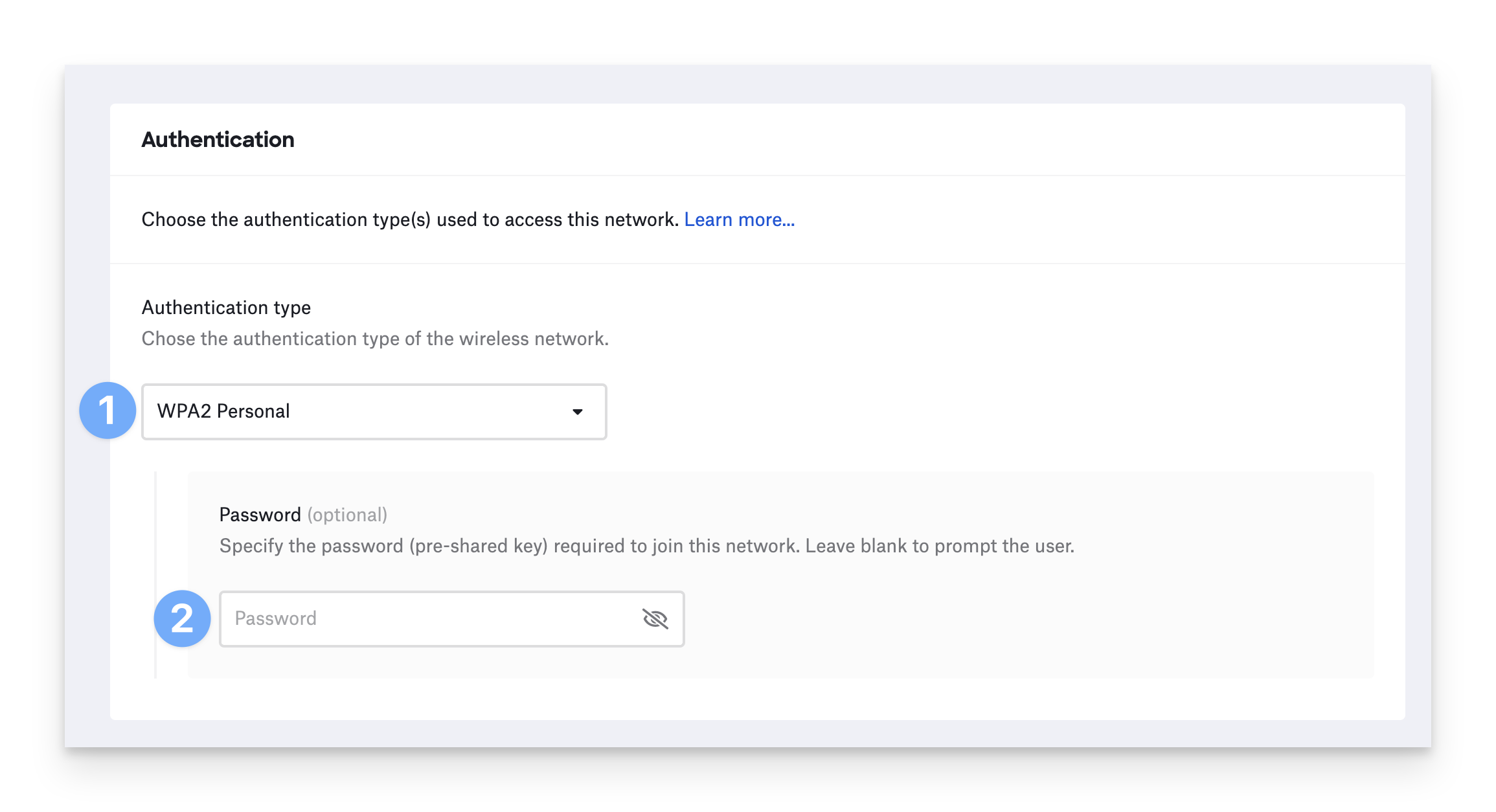
Pre-Shared Key
PSK authentication is commonly used in home and small business environments. Anyone who has the network’s shared password can join it.
For Authentication type, choose WEP, WPA Personal, WPA2 Personal, WPA3 Personal, or Any Personal. Any Personal will work with any of the methods above, and it is useful when some locations use WPA2, and others use WPA3.
Specify the Password. If you do not enter a password, the device prompts the user to enter a password when connecting to the network.
Enterprise Authentication
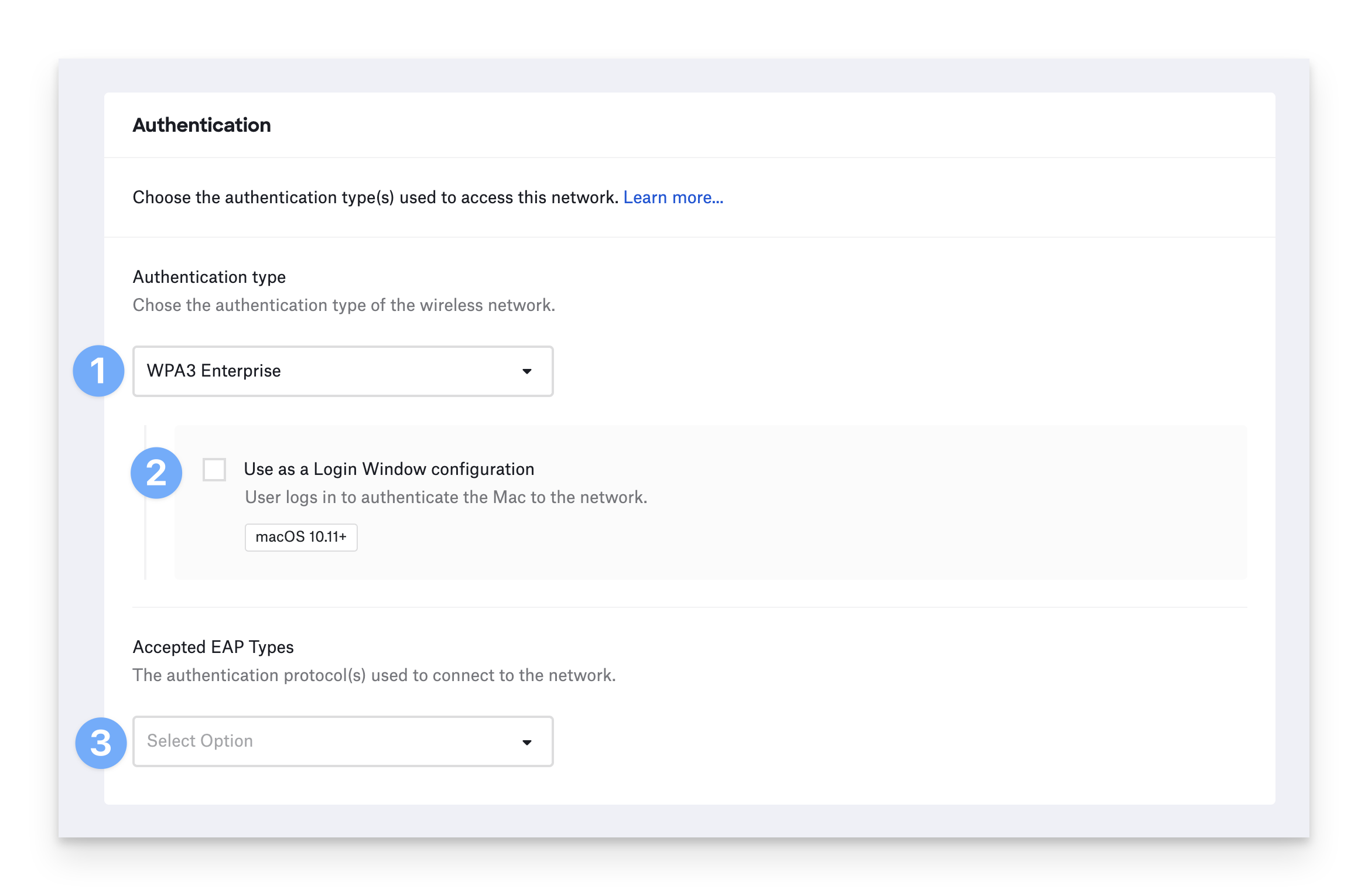
Enterprise authentication uses 802.1X to provide more secure authentication options when connecting to Wi-Fi networks. Enterprise authentication types include Dynamic WEP, WPA Enterprise, WPA2 Enterprise, and WPA3 Enterprise.
For Authentication type, choose Dynamic WEP, WPA Enterprise, WPA2 Enterprise, or WPA3 Enterprise.
On macOS, if you wish to authenticate to the network as the user that logs in at the login window, select Use as a Login Window configuration. Otherwise, the configuration is considered a System configuration, and Mac systems will be able to authenticate to the network when a user has not logged in. You can also use this option in conjunction with EAP-TLS so a certificate identity is used to authenticate the system before login, but then login window credentials are used to authenticate the user.
Using this configuration requires integration with a directory service. See this Apple support article for more information.
Select the Accepted EAP Types your network supports. You may select more than one and will need to set all the settings necessary for the selected EAP types. For more information on configuring specific EAP types, refer to Configure Enterprise Wi-Fi authentication protocols.
Configure an Identity Certificate
You can configure an identity certificate using AD CS, SCEP, or by uploading a PKCS #12 file. For instructions on configuring identity certificates, see our Using Identity Certificates for 802.1X Authentication support article.
Configure Certificate Trust Settings
Specifying trusted certificates in the Wi-Fi Library Item is not recommended. If certificates are renewed or changed, you will need to redeploy the entire Wi-Fi profile, potentially causing devices to disconnect from the Wi-Fi network.Instead, install the trusted certificate chain for your RADIUS server(s) using a separate Certificates Library item. Then specify the name of those certificates in the Wi-Fi Library item under Specify server certificate names. See Apple Platform Deployment for more information.
Most enterprise Wi-Fi environments require that devices trust the 802.1X authentication server(s), typically a Remote Access Dial-In User Server (RADIUS). The Certificate trust settings allow you to configure which certificates presented by the server devices will trust. If a device does not trust the authentication server(s), the user will be prompted to trust it.
Select Specify trusted certificates if you want to provide certificates for the configured devices to trust. Then upload the certificates in .cer or .crt format.
Select Specify server certificate names if you want to provide DNS names of certificates devices should trust. Then enter their DNS names — wildcards are accepted.
Select Allow trust exceptions if you want to ask the user whether to trust the authentication server if the presented certificate fails validation. This option is deprecated in newer versions of macOS and iOS.
.png)
Configure Proxy Settings
Configure devices to use a network proxy by configuring the settings in the Proxy section.
To configure network proxy settings, toggle the Proxy section to Managed.
To configure devices to use a Proxy Auto-Configuration (PAC) file, select Automatic for Proxy type.
Specify the Proxy PAC URL where devices can find the PAC file.
If you want devices to attempt to connect directly to destinations when the PAC file is not available, select Proxy PAC fallback allowed.
.png)
To configure devices to use a specific proxy, choose Manual for Proxy type.
Provide the Proxy server and port.
If the proxy requires authentication, provide the Proxy username and Proxy password.
Configure Fast Lane Marking
Use Fast Lane on networks and devices that support Quality of Service (QoS) marking to prioritize traffic from apps on connected devices as voice, video, or real-time data. To learn more about Fast Lane, refer to iOS Compatibility with Cisco QoS Fastlane & Adaptive 802.11r.
Fast Lane is not supported by all networks or devices.
If you want to manage Fast Lane marking, toggle the Fast Lane marking section to Managed.
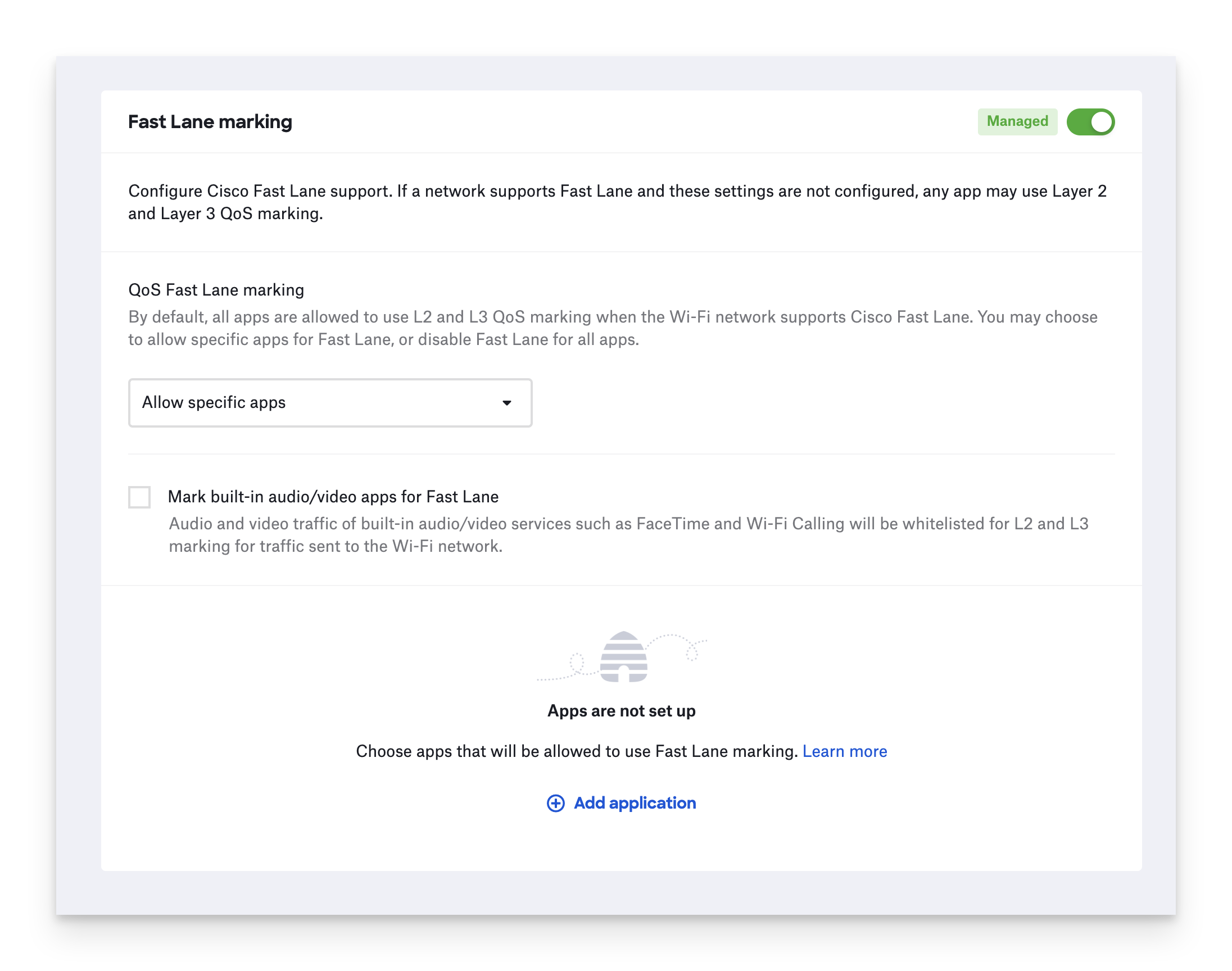
To turn off Fast Lane, choose Disable Fast Lane for all apps.
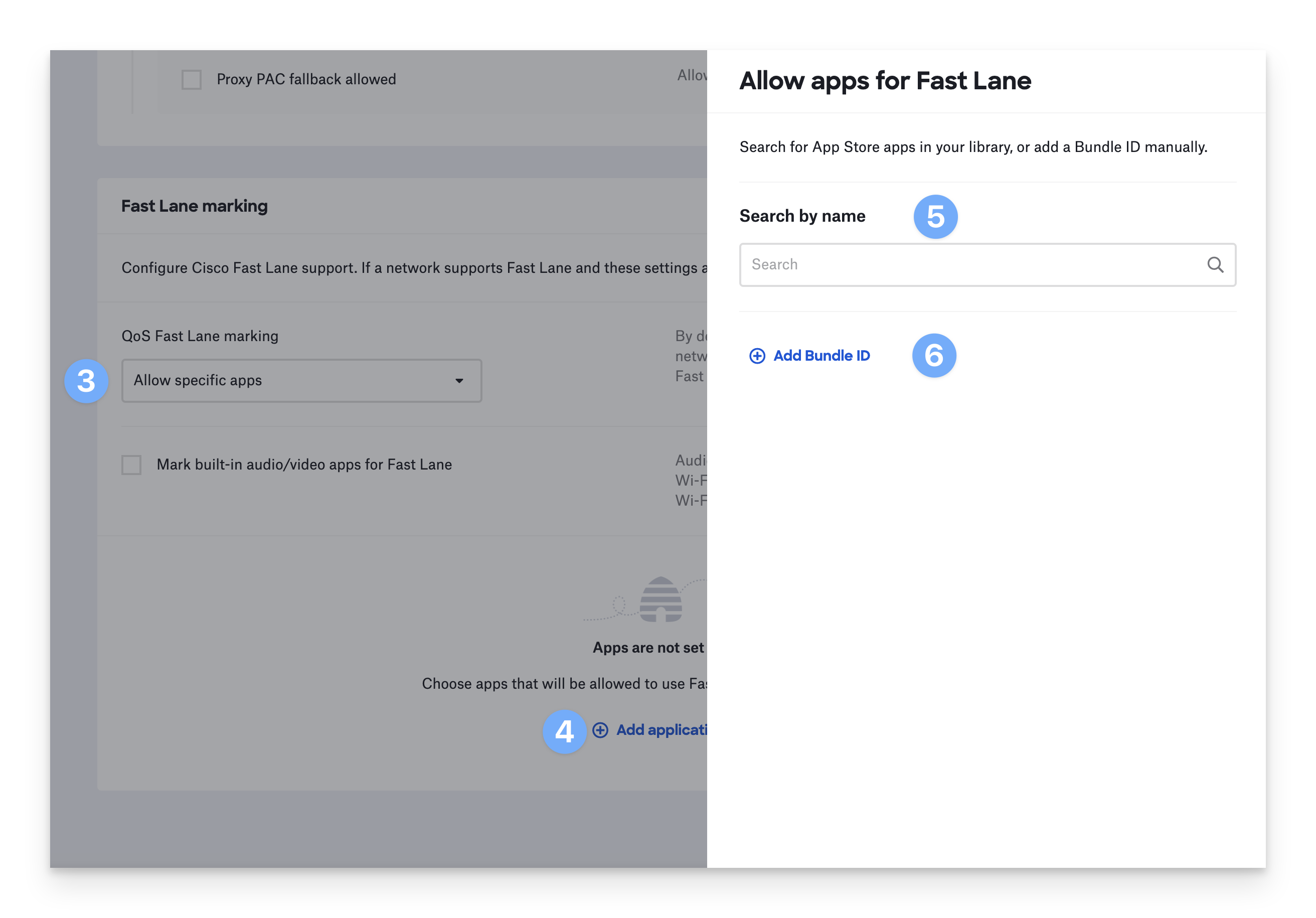
To turn on Fast Lane, choose Allow specific apps.
Fast Lane applies to network traffic from specific apps. Click Add application to add apps to the allow list.
To add apps from your Kandji Library, enter the app’s name under Search by name. Select the apps you want to allow to use Fast Lane.
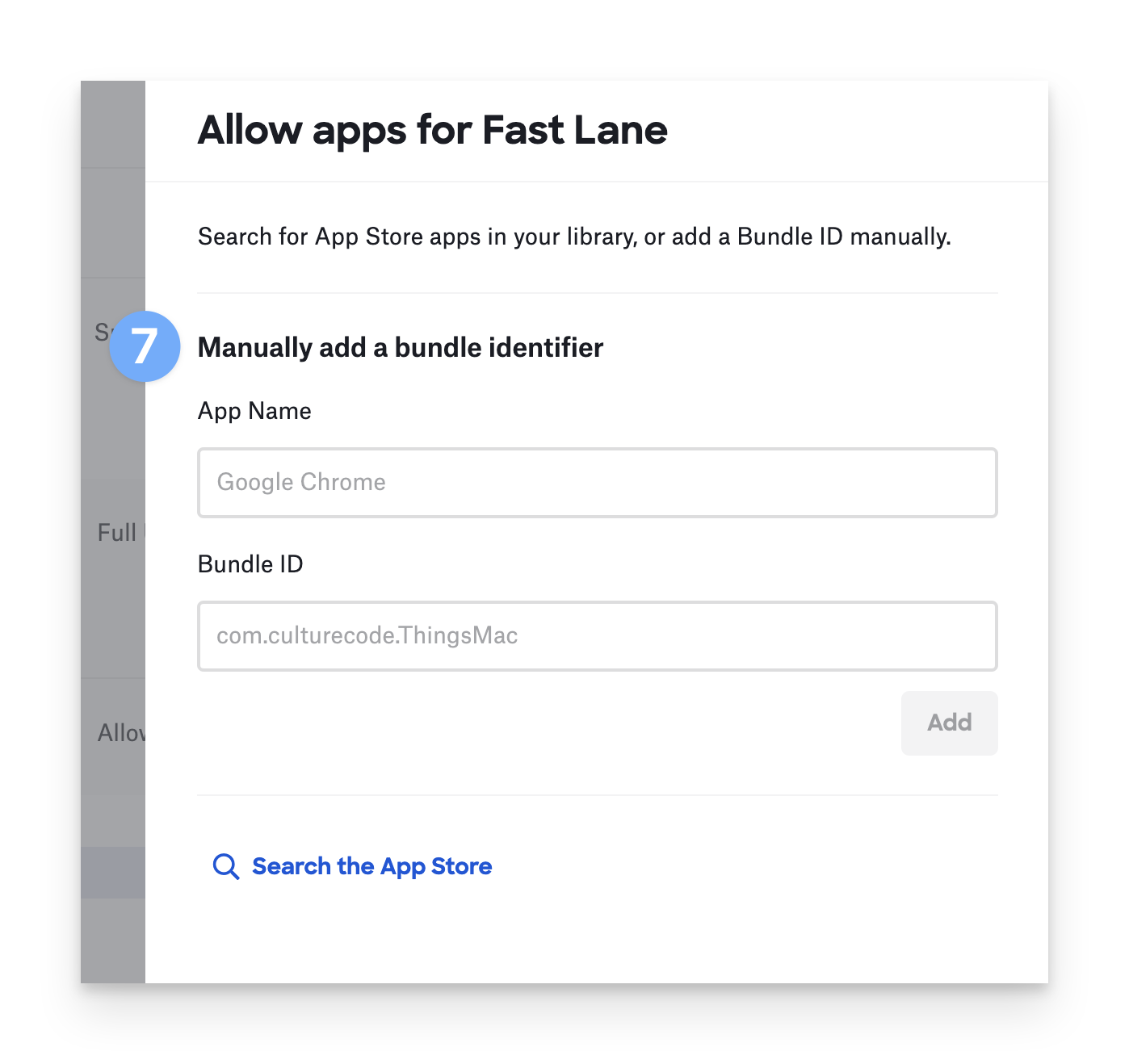
You may also specify apps by Bundle ID. Click Add Bundle ID
Provide the App Name and Bundle ID and click Add. You can add multiple Bundle IDs.
Click Done.